Domestic Expansion Joint Filler Board Road Construction
Price 180.0 INR/ Number
Domestic Expansion Joint Filler Board Road Construction Specification
- Head Code
- Standard
- Max. Temperature
- Up to 70C
- Media
- Concrete, Road Surfaces
- Surface Treatment
- Smooth
- Material
- Bitumen Impregnated Fibre Board
- Technique
- Compressed Fibre Board
- Type
- Expansion Joint Filler Board
- Connecting Type
- Interlocking or Butt Joint
- Shape
- Rectangular
- Working Pressure
- Suitable for Standard Road Loads
About Domestic Expansion Joint Filler Board Road Construction
In road construction, Expansion Joint Filler Boards are critical materials used to accommodate the natural movement of concrete slabs due to thermal expansion, contraction, and other stresses. Here's a breakdown of what they are, why they matter, and the types typically used:
What Is an Expansion Joint Filler Board?
An expansion joint filler board is a compressible sheet material placed between concrete slabs or between concrete and fixed structures to absorb movement and prevent cracking.
Why Is It Used in Road Construction?
-
Thermal Movement: Concrete expands in hot weather and contracts in cold.
-
Prevents Cracking: Without joints, slabs might push against each other and crack.
-
Separation: Provides a buffer between concrete and other structures (like bridges, buildings, or manholes).
Common Materials Used
-
Bitumen-impregnated fiberboard:
-
Traditional material
-
Water-resistant, compressible, durable
-
-
Closed-cell polyethylene foam (e.g., EVA foam):
-
Lightweight
-
Flexible and easy to install
-
-
Cork filler boards:
-
High compressibility
-
Eco-friendly option
-
-
Rubber or neoprene:
-
Used in high-performance areas (like airport runways)
-
Installation Highlights
-
Placed vertically between slabs before the concrete pour.
-
Must align with the joint and extend the full depth of the slab.
-
Sealed on top with a sealant to prevent water and debris infiltration.
Typical Sizes (May Vary by Project)
-
Thickness: 10 mm, 12 mm, 20 mm
-
Height: Matches the slab depth (e.g., 150 mm to 300 mm)
-
Length: Usually comes in 1 or 2 meter lengths
If you're working on or specifying for a road construction project, I can help you choose the right type of filler board based on traffic load, climate, and other specs. Want to dive into standards or pricing in your area?
Superior Durability and Weather Resistance
This expansion joint filler board is crafted with premium bitumen-impregnated fibreboard, ensuring reliable performance even in harsh weather conditions. Its rot-proof and waterproof characteristics make it ideal for long-lasting applications in roads, bridges, and concrete infrastructure. The product maintains its integrity and functionality over time, despite exposure to moisture, temperature fluctuations, and standard road loads.
Precision-Engineered for Road Construction Needs
Designed to accommodate concrete movement and minimize cracking, the filler board comes in precise thicknesses (12 mm, 18 mm, 25 mm) and can be cut to width requirements. Its excellent compression recovery and smooth surface facilitate proper joint filling and ease of installation. Whether for new builds or repairs, the board's robust construction adapts to Indian road standards and demanding construction schedules.
FAQ's of Domestic Expansion Joint Filler Board Road Construction:
Q: How is the Domestic Expansion Joint Filler Board installed in road construction projects?
A: Installation is straightforward: The board is cut to required dimensions and placed between concrete slabs before pouring. It can be fitted using interlocking or butt joints, ensuring a secure and even fit. Its smooth surface and manageable weight make manual handling and positioning easy for workers.Q: What thickness and size options are available for this expansion joint filler board?
A: It is available in standard thicknesses of 12 mm, 18 mm, and 25 mm. The standard length is 2 meters, with optional widths of 500 mm and 1000 mm, or custom sizes as per project requirement. This flexibility makes it suitable for a range of road and bridge construction applications.Q: Where can this filler board be used within infrastructure projects?
A: The expansion joint filler board is ideal for use in concrete pavements, roads, and bridge structures. It is designed to absorb concrete expansion and contraction due to temperature variations, making it essential for all major roadways and urban infrastructure in India.Q: What benefits does this bitumen-impregnated fibreboard offer over traditional materials?
A: This board provides excellent weather resistance, is rot-proof, odorless, and remains structurally sound under varying pressures and temperatures (up to 70C). Its high compression recovery (minimum 70%) maintains joint effectiveness and durability far longer than conventional wood or untreated fibre fillers.Q: When should an expansion joint filler board be installed during the construction process?
A: The filler board must be installed prior to pouring the concrete slabs. It is positioned in the designated joint spaces, ensuring concrete expansion does not lead to cracking or structural damage over time.Q: What is the maximum water absorption rate of the board and why is this important?
A: The board has a maximum water absorption of 15%, minimizing the risk of swelling, disintegration, or reduction in performance. This quality ensures stable joint performance even under wet conditions, which is critical for road and bridge longevity.






Price:
- 50
- 100
- 200
- 250
- 500
- 1000+
More Products in Bellow And Expansion Joint Category
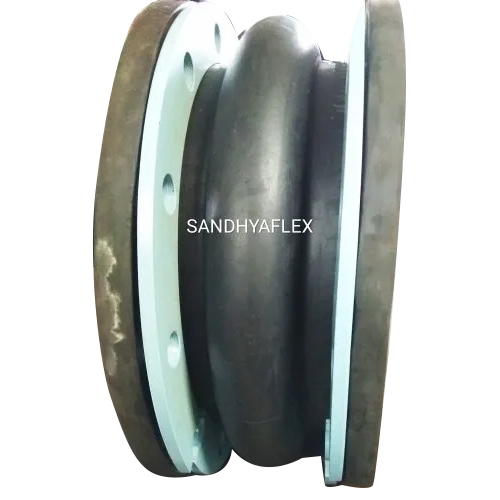
Industrial Rubber Expansion Joint
Price 12000 INR / Unit
Minimum Order Quantity : 100 Units
Product Type : Rubber Expansion Joint
Size : 25mm to 500mm
Usage : Joints (Bellows) in Piping Systems
Surface Treatment : Other, Smooth Rubber Finish
Heavy Duty Rubber Expansion Joint
Price 6000 INR / Piece
Minimum Order Quantity : 100 Pieces
Product Type : Rubber Expansion Joint
Size : 1
Usage : Pipe Connection
Surface Treatment : Other, Black Smooth Surface
F Type Strip Seal Expansion Joint
Price 2800 INR / Meter
Minimum Order Quantity : 100 Meters
Product Type : Strip Seal Expansion Joint
Size : Depth 80 mm
Usage : Bridge Construction
Surface Treatment : Painted
Strip Seal Expansion Joint 16mm
Price 3000 INR / Meter
Minimum Order Quantity : 100
Product Type : Strip Seal Expansion Joint
Size : as per drg
Usage : Bridge Construction
Surface Treatment : Painted

 Send Inquiry
Send Inquiry





 Send Inquiry
Send Inquiry Send SMS
Send SMS