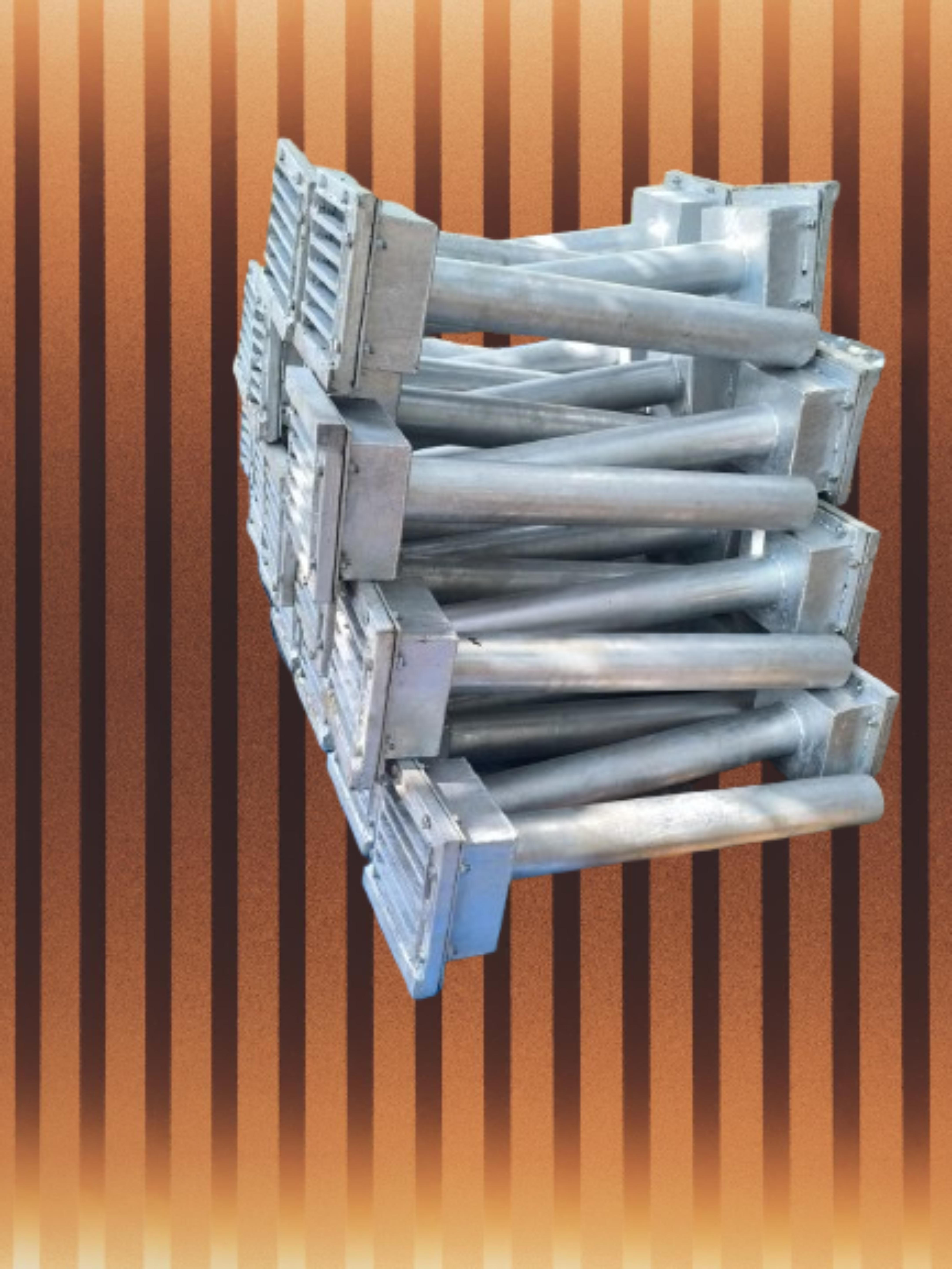
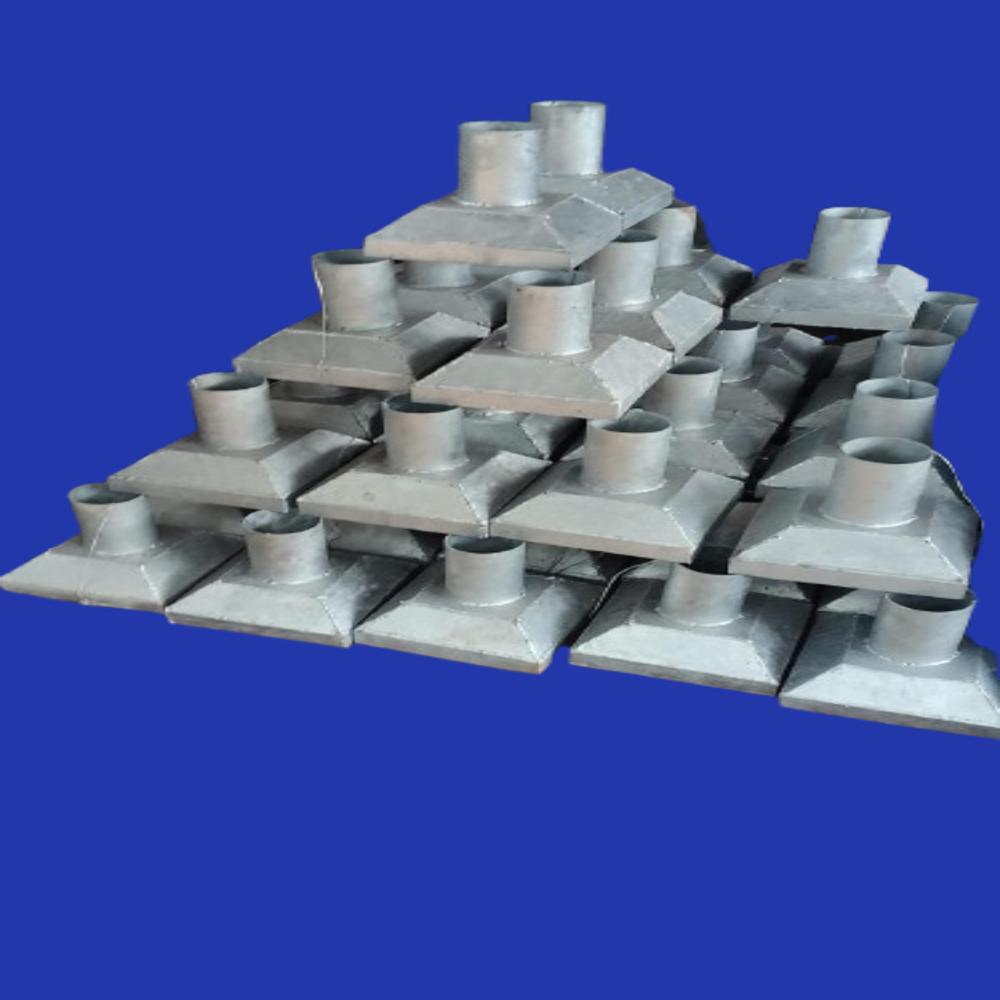
Standard Drainage Spout Bridge
Price 2400.0 INR/ Meter
Standard Drainage Spout Bridge Specification
- Surface Treatment
- Smooth, easy-clean finish
- Installation Type
- Inline, surface-mount
- Usage & Applications
- Bridges drainage pipes, directs rainwater or wastewater flow across surfaces
- Connection
- Push-fit
- Feature
- Corrosion-resistant, durable, lightweight
- Flow Rate
- Designed for high-capacity drainage
- Technology
- Injection moulded construction
- Product Type
- Standard Drainage Spout Bridge
- Plastic Type
- PVC
- Shape
- Rectangular with flanged ends
- Size
- Standard (usually 4-inch width, confirm specific size per requirement)
- Finish
- Glossy
- Color
- White
- Dimensions/Size
- Approx. 200mm x 120mm x 80mm (L x W x H)
- Material
- High-grade PVC plastic
- Compliance/Certification
- Meets ISI/ASTM drainage standards
- Life Expectancy
- >10 years in standard conditions
- UV Resistance
- Yes, suitable for prolonged outdoor exposure
- Maintenance
- Low maintenance, easy to clean with water
- Chemical Resistance
- High, withstands most domestic and industrial chemicals
- Temperature Resistance
- Suitable for outdoor and all-weather use
- Weight
- Approx. 350-500 grams (varies as per size specification)
About Standard Drainage Spout Bridge
A Drainage Spout for Bridges is a structural component designed to direct water away from bridge decks, ensuring proper drainage and helping to maintain the structural integrity of the bridge. These spouts are essential in preventing water from accumulating on the bridge surface, which could lead to erosion, corrosion, or structural damage over time. They are typically positioned at key points along the bridge to allow rainwater or runoff to be directed off the bridge safely and efficiently.
Key Features of a Drainage Spout for Bridges:
| Feature | Details |
|---|---|
| Material | Typically made from stainless steel, cast iron, aluminum, or plastic (for corrosion resistance and durability) |
| Size | Varies depending on the size of the bridge; standard sizes typically range from 50mm to 150mm in diameter |
| Shape | Usually a pipe or trough-style opening, designed to allow water to flow out easily |
| Location | Installed at key points such as bridge abutments, gutter lines, or at expansion joints |
| Water Flow | Designed to direct water off the bridge deck and into drainage systems such as stormwater drains, catch basins, or downspouts |
| Design Features | May include screens or filters to prevent debris from clogging the spout and disrupting the drainage flow |
| Angle and Orientation | Installed at an angle to ensure gravity assists in water flow; can be horizontal or sloped |
Applications:
-
Bridges and Overpasses: To effectively manage runoff water and prevent flooding or water accumulation on the bridge deck.
-
Pedestrian Bridges: Used in areas where pedestrian bridges might accumulate water due to rain or runoff.
-
Highway Bridges: Essential for preventing water buildup and erosion at expansion joints, bridge bearings, and along the bridge span.
-
Railway Bridges: Used to ensure that water runoff doesn't affect the structure or tracks.
-
Parking Decks: Often used in parking garages and other elevated structures to ensure water doesn't pool and damage the surface.
Advantages of a Drainage Spout for Bridges:
-
Prevents Water Damage: Ensures that water is directed away from the bridge deck, reducing the risk of corrosion, rusting, and damage to the bridge structure.
-
Maintains Structural Integrity: Prevents excessive water accumulation, which could lead to the weakening of the bridge's foundation or supporting structures.
-
Protects from Erosion: Directs water to safe drainage points, preventing erosion of the soil around the base or supporting pillars.
-
Reduces Ice Formation: By efficiently draining water off the bridge, it reduces the chances of ice formation during cold weather, which could make the bridge slippery.
-
Improves Safety: Helps keep the bridge deck dry, improving traction for vehicles and pedestrians and reducing the likelihood of accidents due to water accumulation or flooding.
Installation Considerations:
-
Proper Placement: Ensure the drainage spouts are strategically located at points where water is most likely to accumulate, such as expansion joints, at the ends of the bridge, or near drainage channels.
-
Alignment: Install the spouts at the proper angle to allow gravity to facilitate water flow without obstruction.
-
Connection to Drainage Systems: Ensure the spouts are properly connected to stormwater drainage pipes, catch basins, or other drainage channels to direct water flow away from the bridge.
-
Material Durability: Choose materials that are corrosion-resistant, especially if the bridge is located in areas with harsh weather conditions, such as coastal or high-salinity environments.
Materials for Drainage Spouts:
-
Stainless Steel: Commonly used due to its corrosion resistance and strength, ideal for bridges in coastal areas or areas with heavy rainfall.
-
Cast Iron: Strong and durable, often used in older or historic bridges.
-
Aluminum: Lightweight and corrosion-resistant, ideal for smaller or newer bridges.
-
Plastic or PVC: A more affordable option used in non-critical areas, or for temporary drainage solutions.
Maintenance and Cleaning:
-
Regular Inspections: Inspect the spouts periodically to ensure they are free from blockages (like leaves, dirt, or debris).
-
Cleaning: Clean the spouts as needed to prevent clogging, especially after heavy storms.
-
Check for Corrosion: Over time, corrosion can weaken the material, especially in metal spouts. Regular inspections are key to maintaining their effectiveness.
Types of Drainage Spouts:
-
Standard Drainage Spouts: Simple, circular pipe-shaped or trough-style spouts that are typically installed at the edges of the bridge.
-
Adjustable Drainage Spouts: These can be adjusted in length or direction, depending on the bridge's specific drainage needs.
-
Integrated Drainage Systems: In some cases, the drainage spout may be integrated into a more complex system that includes gullies, drain channels, or surface drains.
Would you like further details on a specific type of drainage spout, installation tips, or need help sourcing suppliers for this equipment? Let me know!
Durable, Weather-Resistant Construction
Manufactured from high-grade PVC, the spout bridge boasts excellent temperature, UV, and chemical resistance, ensuring it remains dependable in all climates. The glossy, injection-moulded finish prevents corrosion and simplifies cleaning, further contributing to its longevity. This resilience makes it ideal for both domestic and industrial drainage systems exposed to harsh conditions.
Easy Installation and Versatile Application
Designed with a rectangular, flanged form and push-fit connection, the spout bridge allows for quick inline or surface-mount installation. Its standard 4-inch width and compatible size specifications make it suitable for bridging drainage pipes in varied landscape and architectural projects. Whether you're a supplier, wholesaler, or manufacturer, its universal design fits seamlessly into new or existing systems.
FAQ's of Standard Drainage Spout Bridge:
Q: How is the Standard Drainage Spout Bridge installed in drainage systems?
A: Installation is straightforward due to its push-fit connection and rectangular flanged design. Position the spout bridge inline or surface-mounted between drainage pipes, ensuring a snug push-fit for a leak-proof seal. Always confirm the size to match your specific piping configuration.Q: What makes this drainage spout bridge suitable for outdoor use and all-weather conditions?
A: The bridge is constructed from high-grade PVC with UV and temperature resistance, allowing it to withstand harsh sunlight, rain, and varying temperatures without degrading. Its high chemical resistance also protects it from most domestic and industrial effluents.Q: When should I use a drainage spout bridge in my construction or landscaping project?
A: A drainage spout bridge is ideal when you need to direct rainwater or wastewater across open surfaces, like bridges, decks, or outdoor walkways. It's especially useful where high-capacity drainage and long-lasting, corrosion-resistant materials are required.Q: Where can this product be applied beyond residential drainage?
A: Besides residential use, it's well-suited for commercial, industrial, municipal, and public spaces where the direction of stormwater or wastewater flow is essential. Its compliance with ISI/ASTM standards supports usage in regulated drainage projects.Q: What is the maintenance process and how easy is it to keep clean?
A: The spout bridge has a smooth, glossy surface that resists buildup. Maintenance simply involves rinsing or wiping with water, making it low-maintenance compared to alternatives that may corrode or clog over time.Q: What are the key benefits of using the Standard Drainage Spout Bridge?
A: Key advantages include high durability, resistance to weather and chemicals, effortless installation, long life expectancy, and compliance with major drainage standards. Its lightweight and sleek design makes it convenient for handling and integration into any system.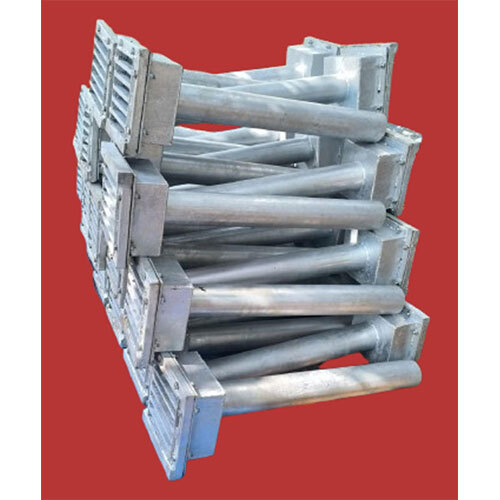






Price:
- 50
- 100
- 200
- 250
- 500
- 1000+
More Products in Drainage Spout Category
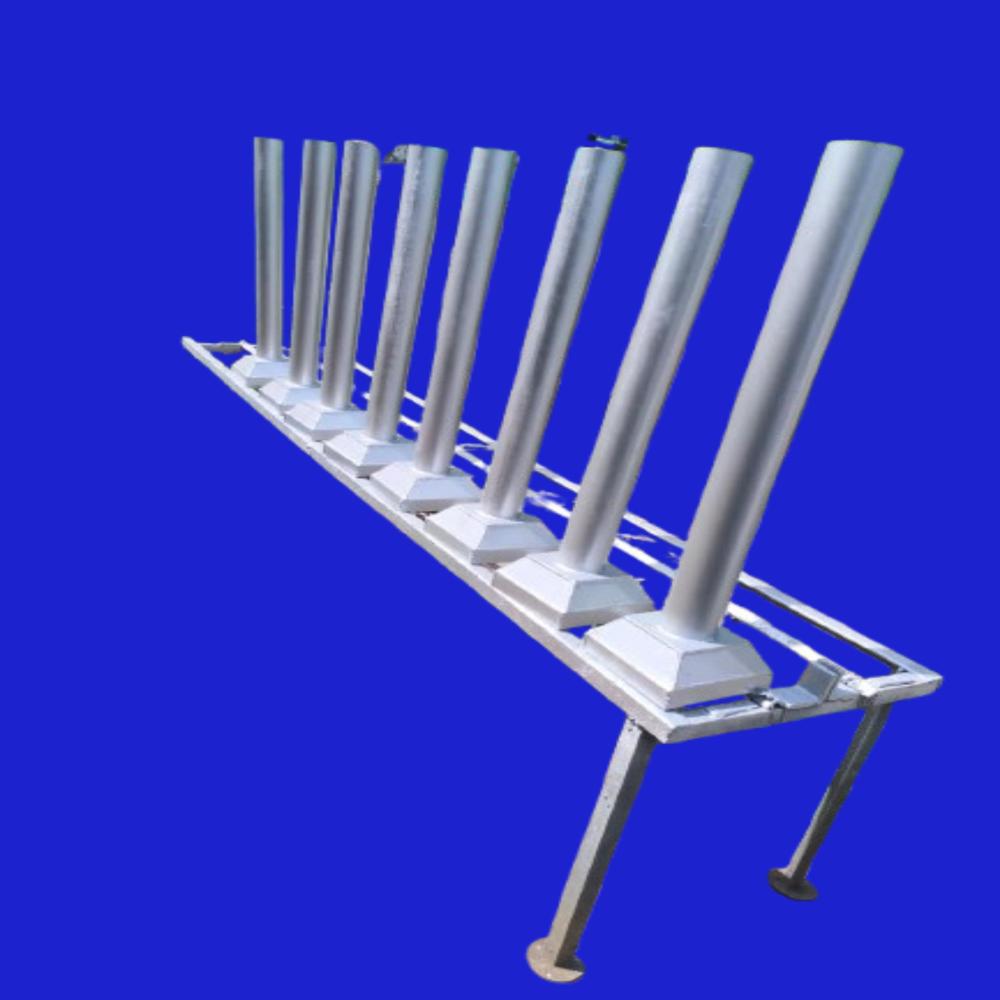
Bridge Drainage Spout
Price 2250 INR / Piece
Minimum Order Quantity : 100 Pieces
Usage & Applications : Bridge drainage, removal of surface water
Color : Silver
Shape : Round
Product Type : Bath Hardware Sets
GI Galvanised Drainage Spout
Price 2000.0 INR / Number
Minimum Order Quantity : 1 Number
Usage & Applications : Drainage, Rainwater outlet, Roof and Gutter spout
Color : Silver
Shape : Other, Rectangular with Slanted End
Product Type : Other, Drainage Spout
Deep Galvanized Drainage Spout
Price 2500.0 INR / Piece
Minimum Order Quantity : 1 Piece
Usage & Applications : Channelizing and draining roof or terrace waters
Color : Silver
Shape : Round
Product Type : Squat Pans
Drainage Spout
Price 1600.0 INR / Number
Minimum Order Quantity : 1 Number
Usage & Applications : Rainwater drainage, Gutter outlet, Roof drainage systems
Color : White
Shape : Rectangular
Product Type : Other, Drainage Spout

 Send Inquiry
Send Inquiry





 Send Inquiry
Send Inquiry Send SMS
Send SMS Call Me Free
Call Me Free